Chemical Synthesis
appreciate that chemical synthesis involves the selection of particular reagents to form a product with specific properties
- Chemical synthesis processes involve selecting specific reagents and reaction conditions to optimise the rate and yield of the product.
understand that reagents and reaction conditions are chosen to optimise the yield and rate for chemical synthesis processes, including the production of ammonia (Haber process), sulfuric acid (contact process) and biodiesel (base-catalysed and lipase-catalysed methods)
Haber process
- The Haber Process is the production of ammonia
- The formation of ammonia occurs naturally with nitrogen fixing bacteria known as nitrogenase (enzyme)
As temperature increases, Kc decreases.
Although the reaction is exothermic, which would imply that a lower
temperature is required for the forward reaction to be favoured, by
lowering the temperature, the reaction yield would decrease. This is
because at lower temperatures, the rate of reaction decreases because
there is not enough energy in the system for the collisions to exceed
the activation energy. Therefore, a moderate temperature is required,
so that the rate of reaction and reaction yield are maximised, and this
is achieved by temperatures from 400-500oC.
Contact process
- The contact process is the formation of sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
understand that fuels, including biodiesel, ethanol and hydrogen, can be
synthesised from a range of chemical reactions including, addition, oxidation
and esterification
describe, using equations, the transesterification of triglycerides to
produce biodiesel
- Biodiesel is a fatty acid alkyl ester made from fats and oils
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
Transesterification
- Reaction
understand that fuels, including biodiesel, ethanol and hydrogen, can be
synthesised from a range of chemical reactions including, addition, oxidation
and esterification
describe, using equations, the production of ethanol from fermentation and
the hydration of ethene
understand that enzymes can be used on an industrial scale for chemical
synthesis to achieve an economically viable rate, including fermentation to
produce ethanol and lipase-catalysed transesterification to produce biodiesel
Hydration of ethene
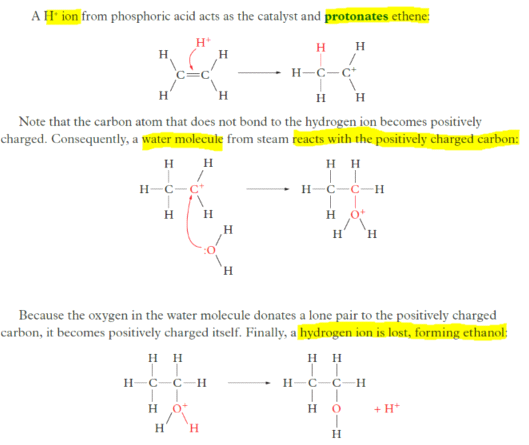
understand that fuels, including biodiesel, ethanol and hydrogen, can be
synthesised from a range of chemical reactions including, addition, oxidation
and esterification
discuss, using diagrams and relevant half-equations, the operation of a
hydrogen fuel cell under acidic and alkaline conditions.
calculate the yield of chemical synthesis reactions by comparing
stoichiometric quantities with actual quantities and by determining limiting
reagents.
- Limiting reagent is the reactant in a chemical reaction that determines how much of the products are made
- Percentage yield in a multistep synthesis is the product of the percentage yield for each individual reaction